Deciding to undergo fertility treatment can be overwhelming, but understanding your treatment options can make the process easier.
Two of the most commonly used fertility treatments are intrauterine insemination (IUI) and in vitro fertilization (IVF). While both treatments can help couples conceive, each works in its own way and has varying benefits and potential drawbacks.
This article explores the differences between IUI and IVF, including the pros and cons of each treatment option and how to determine which one is right for you.
Common Fertility Treatments Explained
Individuals or couples who are struggling with fertility have several options available to them, including:
- Medication: Common fertility medications include clomiphene and letrozole— which is especially effective for individuals with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
- Surgery: Surgery can address reproductive organ blockages, abnormalities, and underlying conditions like endometriosis that affect fertility.
- Assisted reproductive technology (ART): Options such as intrauterine insemination (IUI) or in vitro fertilization (IVF) are also available. Additional options like intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) can be paired with IVF to increase success rates.
IUI vs. IVF: Which is best for you?
When choosing between IUI and IVF, it’s important to consider the individual’s age, fertility issues, cost, and personal preference. This section highlights the pros and cons of each treatment option and how to determine which one is right for you.
What’s the difference between IUI & IVF?
IUI and IVF are distinct fertility treatments. IUI inserts sperm directly into the woman’s uterus, while IVF involves fertilizing eggs with sperm outside the body before placing them back into the uterus.
IUI vs. IVF: Pros & Cons
This section highlights the pros and cons of each procedure to help guide your decision-making process.
Intrauterine Insemination (IUI)
Pros:
- Less invasive compared to IVF
- Relatively inexpensive when compared to IVF
- Higher success rate as compared to regular intercourse
- Quick outpatient procedure (5-10 minutes)
Cons:
- Requires clear fallopian tubes, ovulation, and motile sperm
- A success rate of around 10%-15% per cycle, depending on factors such as age and cause of infertility, is lower compared to IVF
- Increased risk of multiple pregnancies
- Possible side effects from fertility drugs include mood swings, hot flashes, breast tenderness, nausea, bloating, headaches, swelling, painful and swollen ovaries, pelvic discomfort, and ovarian cysts
- Not effective for treating underlying fertility issues like endometriosis or male factor infertility
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF)
Pros:
- Addresses reproductive medical conditions such as blocked fallopian tubes
- Bypasses male-factor infertility with intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI)
- Decreased risk of multiple pregnancies (twins, triplets) with Single Embryo Transfer (SET)
- Prevents single-gene disorders through genetic testing of embryos
- The highest chance of achieving a successful pregnancy
- Allows for preemptive genetic testing of the embryo to improve pregnancy rates
- Offers future family planning through freezing excess embryos
- Provides family-building options for the LGBTQ community via donor eggs, donor sperm, etc.
Insurance coverage for in vitro fertilization (IVF) varies widely among states and insurance plans. While some states mandate coverage, eligibility requirements and costs vary. Check with your insurance provider to understand what treatments are covered and what costs you may be responsible for.
Cons:
- Cost – U.S. average is $12,000 – $14,000 per cycle
- More invasive and time-consuming
- Requires multiple doctor visits to monitor hormone levels and egg development
- Possible side effects from fertility drugs
- Physically and emotionally demanding
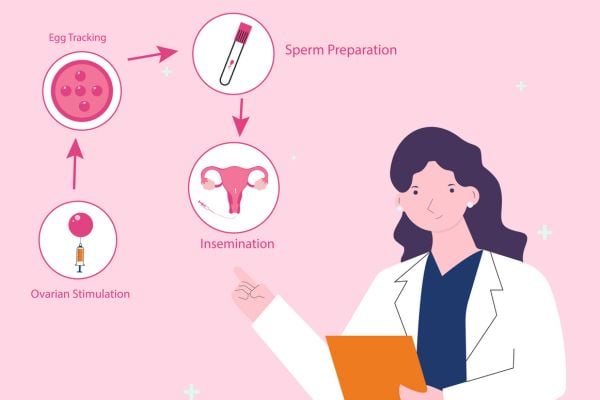
What is Intrauterine insemination (IUI)?
Intrauterine insemination (IUI) is a type of artificial insemination used to treat infertility. Compared to other fertility treatments, IUI is relatively simple. During an IUI procedure, a catheter is placed into the uterus to insert sperm directly into the uterus. This procedure is less invasive than IVF and can be performed as an outpatient procedure with little recovery time.
Who Needs IUI?
IUI may be beneficial for couples experiencing infertility due to the following:
- Anovulation: When an egg does not release from the ovary during a menstrual cycle.
- Asthenozoospermia: When sperm motility is low or poor, or the male partner’s sperm cannot swim properly.
- Cervical factor infertility: When the cervical mucus is too thick for sperm to penetrate.
- Unexplained fertility: When there is no identifiable cause of infertility despite extensive testing.
IUI is recommended for:
- Mild male infertility (low sperm motility)
- Erectile dysfunction or other ejaculation issues
- Mild endometriosis
- Anovulation or irregular ovulation
- Cervical factor infertility
- The need for a sperm donor
- Unexplained infertility
The IUI Procedure Explained
Natural conception can be challenging, but IUI offers a minimally invasive option for individuals and couples hoping to get pregnant. Here’s what to expect, starting with preparation.
Preparing for IUI
IUI preparation involves washing the semen to separate active sperm or thawing frozen donor sperm. Timing is critical, so monitoring ovulation is essential, which can be done through ovulation predictor kits or transvaginal ultrasound imaging. Some patients may receive an HCG injection or medications to induce ovulation at the ideal time. To optimize the chances of conception, IUI should occur one to two days after ovulation.
IUI Medications
Couples with male factor infertility or unexplained infertility may benefit from ovarian stimulation medications. Some doctors may prescribe pre-procedure medications, such as Clomid or Letrozole, to stimulate ovulation, while others may recommend injectable gonadotropins to increase the number of eggs produced. An ovulation trigger shot, usually hCG or Lupron, is another injectable option to help trigger ovulation at the optimal time. The use of add-ons is determined on a case-by-case basis, and not every person undergoing IUI will require them.
The IUI Procedure
A “natural IUI cycle” (an IUI cycle done without fertility drugs) typically takes 15 to 20 minutes and is performed at a fertility clinic or doctor’s office.
The procedure involves the following steps:
- The patient lies on an exam table with their legs in stirrups.
- The doctor inserts a speculum into the vagina.
- A vial of healthy sperm is attached to a thin, flexible catheter by the doctor or nurse.
- The catheter is inserted through the vagina, cervical opening, and uterus.
- Sperm is pushed through the catheter and into the uterus.
- The speculum and catheter are removed.
- After the procedure, the patient can resume normal activities. Light spotting may occur for a day or two.
After the IUI Procedure
After the IUI procedure, continue monitoring for signs of pregnancy and follow any instructions provided by the doctor or fertility clinic. The success of IUI varies depending on an individual’s age, overall health, and fertility, so it’s important to have realistic expectations and to be prepared for multiple attempts if needed.
Where do I find a sperm donor for IUI?
For individuals and couples using donor sperm for IUI, finding a suitable donor can be a complex and personal process. Here are a few options to consider:
- Sperm banks: Sperm banks offer a range of donor sperm options and provide detailed information on donors, including their medical history, physical attributes, and personal interests. To prevent sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), the FDA and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend using frozen semen from a licensed sperm bank.
- Known donors: Some individuals or couples choose to use sperm from someone they know personally, such as a friend or family member. In this case, consider the potential emotional and legal implications carefully and ensure that the donor undergoes medical testing to rule out infectious diseases.
- Anonymous donors: There are services where individuals can connect with potential sperm donors for a fee. It’s important to exercise caution and thoroughly research any potential donor before proceeding with an arrangement. When working with a fertility clinic, your doctor and care team will organize this for you.
Anonymous Sperm Donor vs. Known Sperm Donor
Choosing between an anonymous or known sperm donor is a personal decision for individuals and couples undergoing IUI.
If considering a known donor for IUI, follow these guidelines:
- Know and follow state laws on sperm donation strictly.
- Communicate clearly with the donor about the arrangement’s expectations, boundaries, and legal implications.
- Ensure the donor has undergone medical testing to rule out STDs and genetic disorders.
- Have the donor supply the sperm sample to the physician for medical and legal reasons.
- Ensure that any consent forms are in line with the intended parental status.
- Avoid verbal agreements, and have agreements drawn up by an attorney and signed by both parties.
- Your care team will help organize everything you need when using an anonymous donor.
What can I do to increase the success of an IUI cycle?
There are several steps individuals and couples can take to improve their chances of pregnancy with IUI, including:
- Find a reputable reproductive endocrinologist who prioritizes your best interests.
- Adopt a healthy lifestyle that includes a balanced diet, moderate exercise, and abstaining from smoking and excessive drinking.
- Prioritize stress management and relaxation through meditation, yoga, or a warm bath with scented candles.
- Ensure that the IUI procedure is performed optimally during your menstrual cycle.
IUI Success Rates
IUI success rates vary widely depending on the individual’s age, underlying fertility issues, and personal circumstances, and it may take several cycles of IUI to achieve pregnancy.
Age
A person’s age impacts the number of eggs, egg quality, and overall fertility. This can influence the chances of success with IUI. For individuals under 35, the success rate is typically around 10-15% per cycle. However, for individuals over 35, the success rate tends to be lower, around 8-10% per cycle. Some data suggest that after age 44, the success for IUI is below 1%.
Other Factors
Several factors, including low sperm count, tubal blockage, endometriosis, and PCOS, can influence the success rate of IUI. Poor sperm quality can also decrease the chances of fertilization and pregnancy. In some cases, up to four to six cycles of IUI may be recommended to increase the chances of pregnancy. Still, the number of cycles needed varies depending on the individual’s situation.
IUI Risks & Common Symptoms
IUI is generally a safe procedure, but like all medical treatments, it carries some risks.
Risks
Some of the possible risks of IUI include:
- Multiple pregnancies: IUI increases the risk of multiple pregnancies, such as twins or triplets. This is because the procedure can stimulate the ovaries to release more than one egg.
- Ectopic pregnancy: An ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, typically in the fallopian tube.
- Cramping and spotting: Mild cramping and spotting are common after an IUI procedure.
Common Symptoms
Common symptoms of IUI include mild cramping, spotting, or light bleeding that usually lasts for a few days, bloating and discomfort due to ovarian stimulation medications, and hormonal changes that can cause mood swings and other emotional symptoms.
IUI Cost: Coverage & Experience
IUI cost varies depending on the clinic, location, and need for ovulation-stimulating medications. Depending on the provider, it can range from $300 to $4,000.
Insurance coverage varies, with some plans covering the procedure, while others cover only medications or neither. Some clinics offer discounts or payment plans, and some states have programs for financial assistance.
What is In-Vitro Fertilization (IVF)?
In-vitro fertilization (IVF) is a fertility treatment where eggs are removed from the ovaries and fertilized with sperm in a laboratory. The resulting fertilized eggs (embryos) are then transferred into the uterus. Unlike IUI, fertilization occurs outside the body, giving practitioners more control over embryo selection to increase the chance of a successful pregnancy. IVF typically has a higher success rate than IUI, but it also comes with higher costs and more invasive procedures.
Who Needs IVF?
IVF may be beneficial for couples experiencing infertility due to the following:
- Tubal factor infertility: When the fallopian tubes are blocked or damaged, hindering fertilization and implantation of the embryo.
- Severe male infertility: When the male partner has a very low sperm count, poor sperm motility, or sperm that can’t fertilize the egg by themselves.
- Endometriosis: When endometrial-like tissue grows outside of the uterus, leading to scarring and adhesions that can prevent fertilization and implantation of the embryo.
- Ovarian factor infertility: When the female partner has a low ovarian reserve, poor egg quality, or premature ovarian failure.
- Unexplained infertility: When there is no identifiable cause of infertility despite extensive testing or unsuccessful attempts with other fertility treatments.
IVF is recommended for:
- Tubal factor infertility
- Severe male infertility
- Endometriosis
- Ovarian factor infertility
- Unexplained infertility
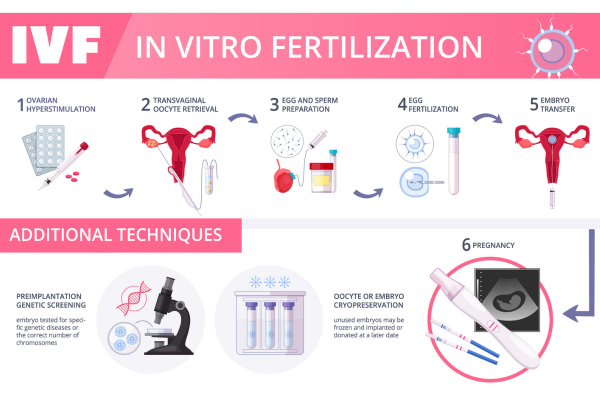
The IVF Procedure Explained
IVF is an invasive procedure that involves multiple steps. Here’s what to expect during an IVF cycle:
Preparing for IVF
Before starting an IVF cycle, the female partner undergoes hormone therapy to stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs, a physical exam to check the reproductive organs, an ultrasound, genetic testing (if needed), and screening for infectious diseases such as HIV and hepatitis.
IVF Treatment Options
Fertility specialists may suggest additional procedures to improve the odds of a healthy and successful pregnancy. Options may include Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) for male infertility, preimplantation genetic testing (PGT) to identify genetic defects in embryos, assisted hatching, single embryo transfer (SET), and frozen embryo transfer (FET).
The IVF Procedure
Unlike IUI, IVF involves the fertilization of eggs outside the body. It’s a complex and multi-step process.
Here’s a condensed summary of the IVF process:
- Ovarian stimulation: Administer hormonal medication for ovarian stimulation for 10-14 days while monitoring progress through ultrasound scans and blood tests. Inject a final hormone to mature the oocytes (eggs), and then schedule an egg retrieval procedure in the fertility clinic 36 hours later.
- Egg retrieval: The doctor retrieves the eggs by accessing the ovaries through the vaginal canal under light sedation. The doctor punctures each follicle containing an egg and aspirates the fluid with a very fine needle. After resting briefly, the patient can go home with an escort and usually returns to normal the following day.
- Egg fertilization: The laboratory uses Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI) to select the best sperm and inject it into each egg individually.
- Embryo culture: The embryologists culture the developing embryos in the laboratory for five to six days until they reach the blastocyst stage of development, which involves the growth of about 200 cells.
- Preimplantation Genetic Testing for Aneuploidy (PGT-A): After reaching the blastocyst stage, doctors conduct Preimplantation Genetic Testing for Aneuploidy (PGT-A) on the embryos to determine their chromosome count. During testing, a small portion of the embryos undergoes a biopsy, and the remaining embryos are frozen. A recent study conducted at RMA has confirmed that an embryo biopsy does not harm the embryo or reduce the probability of implantation. Genetically normal embryos are more likely to lead to healthy and successful pregnancies.
- Frozen Embryo Transfer (FET): Doctors identify a genetically normal embryo for transfer and wait for the endometrium to be ready for Frozen Embryo Transfer (FET) at the right time for the uterus to accept the embryo. FET has a higher likelihood of pregnancy than fresh embryo transfer. RMA clinics use FET as the standard of care for all IVF patients for improved obstetrical outcomes. The procedure is relatively quick; one normal embryo is transferred into the patient’s uterus. The IVF due date can be roughly calculated if no issues arise.
IVF Success Rates
The average likelihood of live birth after transferring a single, genetically normal blastocyst varies by clinic. You can view RMA’s IVF success rates here. Fertility clinics in the US are legally required to report their success rates to the CDC, which includes live birth rates and other outcomes. The Society for Assisted Reproductive Technology also reports on these statistics.
IVF Risks & Common Symptoms
The most notable risk of IVF treatment is multiple births, which may lead to complications. Multiple births can result in low birth weight, premature delivery, and post-natal complications. However, PGT-A testing and Single Embryo Transfer (SET) have reduced the risk. Doctors can confidently transfer one normal embryo with SET, reducing the risk of multiple births. RMA exclusively uses Single Embryo Transfer, transferring only a single healthy embryo.
IVF Cost: Coverage & Experience
IVF costs more than IUI, but IVF delivers the highest pregnancy rates per cycle. The exact cost will depend on your personal treatment program. You can find some ballpark figures on the Society for Assisted Reproductive Technology or read our blog: The Real Cost of IVF.
Coverage for infertility treatment varies from patient to patient and from one insurance provider to another. RMA provides an informational guide to insurance coverage details and a reference list of questions to ask your insurance provider.
Discuss Your Options with a Medical Professional
Our team at RMA is ready to support you in exploring your options. Whether you want to learn more about IUI and IVF or discuss any questions, our physicians are here to help. Use our website links to find your nearest clinic, or complete our online contact form.
A Word from RMA Network
We understand that fertility issues can be overwhelming and emotional. That’s why we’re here to support you throughout your journey. Our expert team of physicians can discuss your options, from IUI to IVF, and help you make the best decision for your unique situation.
Remember, the sooner you take that first step and reach out to us, the sooner we can help you take the next step toward your dream of parenthood.